Cyber Security(Part-1)
Cyber Crime :
Cybercrime is defined as a crime in which a computer is the object of the crime (hacking, phishing, spamming) or is used as a tool to commit an offense (child pornography, hate crimes). Cyber criminals may use computer technology to access personal information, business trade secretsor use the internet for exploitative or malicious purposes. Criminals can also use computers for communication and document or data storage. Criminals who perform these illegal activities areoften referred to ashackers.
Cybercrime may also be referred to as computer crime
Mobile, Wireless Devices and hand-held devices :
Fig: Mobile wireless devices and hand-held devices
- Portable Computer :
It is a general-purpose computer that can be easily moved from one place to another, but cannot be used while in transit, usually because it requires some “setting-up” and an AC power source.
- Tablet PC :
It lacks a keyboard, is shaped like a slate or a paper notebook and has features of a touch-screen with a stylus and handwriting recognition software. Tablets may not be best suited for applications requiring a physical keyboard for typing, but are otherwise capable of carrying out most tasks that an ordinary laptop would be able toperform.
- Internet Tablet :
It is the Internet appliance in tablet form. Unlike a Tablet PC, the Internet tablet does not have much computing power and its applications suite is limited. Also it cannot replace a general-purpose computer. The Internet tablets typically feature an MP3 and video player, a Web browser, a chat application and a picture viewer.
- Personal Digital Assistant(PDA) :
It is a small, usually pocket-sized, computer with limited functionality. It is intended to supplement and synchronize with a desktop computer, giving access to contacts, address book, notes, E-Mail nd otherfeatures.
- Ultra Mobile PC :
It is a full-featured, PDA-sized computer running a general-purpose operating system.
- Smartphone :
It is a PDA with an integrated cell phone functionality. Current Smartphones have a wide range of features and installable applications.
- Carputer :
It is a computing device installed in an automobile. It operates as a wireless computer, sound system, and global positioning system (GPS) and DVD player. It also contains word processing software and is Bluetooth compatible.
- Fly Fusion PentopComputer :
It is a computing device with the size and shape of a pen. It functions as a writing utensil, MP3 player, language translator, digital storage device andcalculator.
Trends in Mobility :
Mobile computing is moving into a new era, third generation (3G), which promises greater variety in applications and have highly improved usability as well as speedier networking. “iPhone” from Apple and Google-led “Android” phones are the best examples of this trend and there are plenty of other developments that point in this direction. This smart mobile technology is rapidly gaining popularity and the attackers (hackers and crackers) are among its biggest fans.
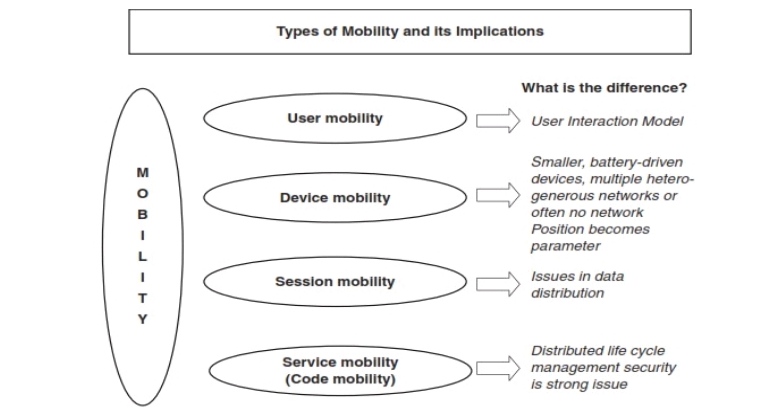
Fig : Mobility types and implications.
- Key Findings for Mobile Computing SecurityScenario
1. With usage experience, awareness of mobile users gets enhanced
2. People continue to remain the weakest link for laptop.
3. Wireless connectivity does little to increase burden of managing laptops.
4. Laptop experience changes the view of starting a smart hand-held pilot.
5. There is naivety and/or neglect in smart hand-held security.
6. Rules rather than technology keep smart hand-held usage in check.
- Popular types of attacks against 3G mobile network :
1. Malwares, viruses and worms.
2. Denial-of-service(DoS).
3. Over billing attack.
4. Spoofed policy development process(PDP).
5. Signaling-level attacks.
Authentication Service Security :
- There are two components of security in mobile computing: security of devices and security in networks.
- A secure network access involves mutual authentication between the device and the base stations or Webservers.
- This is to ensure that only authenticated devices can be connected to the network for obtaining the requested services.
- No Malicious Code can impersonate the service provider to trick the device into doing something it does not meanto.
- Thus, the networks also play a crucial role in security of mobile devices. Some eminent kinds of attacks to which mobile devices are subjected to are: push attacks, pull attacks and crash attacks.
- Authentication services security is important given the typical attacks on mobile devices through wireless networks:DoS attacks, traffic analysis, eaves dropping, man- in-the-middle attacks and session hijacking.